you position:Home > us stock market live > us stock market live
Understanding the Stock Market to GDP Ratio in the US
![]() myandytime2026-01-23【us stock market today live cha】view
myandytime2026-01-23【us stock market today live cha】view
info:
The stock market to GDP ratio, often referred to as the "Shiller P/E" or "Cyclically Adjusted Price-to-Earnings Ratio," is a crucial metric that investors and economists use to gauge the valuation of the stock market relative to the overall economy. In this article, we delve into the stock market to GDP ratio in the United States, exploring its significance, historical trends, and implications for investors.
What is the Stock Market to GDP Ratio?
The stock market to GDP ratio is calculated by dividing the total value of the stock market by the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. This ratio provides insight into how much of the country's economic output is being invested in the stock market. A high ratio suggests that the stock market is overvalued, while a low ratio indicates that it is undervalued.
Historical Trends in the US Stock Market to GDP Ratio
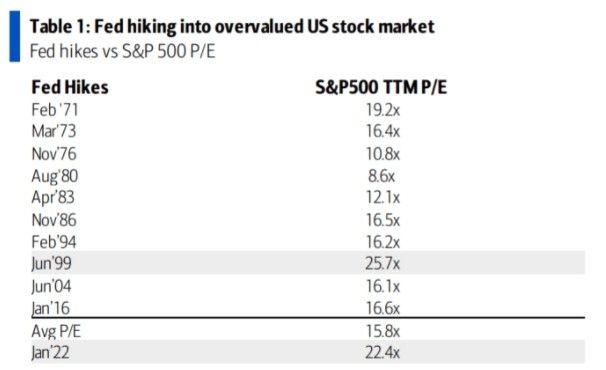
Historically, the stock market to GDP ratio in the United States has fluctuated widely. Over the past century, the ratio has ranged from around 5 to over 30. The highest point in history occurred in the late 1920s, just before the Great Depression, and again in the late 1990s, during the dot-com bubble.
One notable trend is the long-term increase in the stock market to GDP ratio since the early 1980s. This trend can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Increased Stock Market Participation: The rise of 401(k) plans and other retirement accounts has encouraged more Americans to invest in the stock market.
- Economic Growth: The US economy has experienced significant growth over the past few decades, leading to higher corporate earnings and, consequently, higher stock prices.
- Low Interest Rates: Central banks around the world, including the Federal Reserve, have maintained low interest rates for an extended period, making stocks more attractive relative to bonds and other fixed-income investments.
Implications for Investors
Understanding the stock market to GDP ratio can help investors make more informed decisions about their investments. Here are a few key implications:
- Overvaluation: If the stock market to GDP ratio is above its historical average, it may indicate that the market is overvalued. This could be a sign of potential future declines in stock prices.
- Undervaluation: Conversely, if the ratio is below its historical average, it may suggest that the stock market is undervalued, presenting a buying opportunity for investors.
- Market Timing: By analyzing the stock market to GDP ratio over time, investors can identify periods when the market may be particularly vulnerable or attractive.
Case Studies
One notable case study is the tech bubble of the late 1990s. During this period, the stock market to GDP ratio soared to over 30, reaching its highest level in history. As a result, many investors lost significant amounts of money when the bubble burst and stock prices plummeted.
Another example is the current stock market, which has seen a significant increase in the stock market to GDP ratio over the past few years. This has led some experts to question whether the market is currently overvalued and whether investors should be cautious.
Conclusion
The stock market to GDP ratio is a valuable metric for investors and economists alike. By understanding this ratio, investors can gain insight into the valuation of the stock market relative to the overall economy and make more informed decisions about their investments. As always, it's important to consider a range of factors when evaluating the stock market and making investment decisions.
so cool! ()
last:Carnival Corporation & PLC: A Deep Dive into the US Stock Market
next:nothing
like
- Carnival Corporation & PLC: A Deep Dive into the US Stock Market
- Dow Jones Real Time Chart: Unveiling the Financial Pulse
- Recent News on Penny Stocks: A Glimpse into the US Market
- Stock Market in USA Today: Key Trends and Predictions
- Dow Jones Premarket Today: A Comprehensive Guide to Today's Market Trends
- Stock Market Now CNN: Your Ultimate Guide to Understanding the Latest Trends and
- Mastering Stock Market Equity: Your Ultimate Guide to Financial Success"
- Top Stocks in the US Market: Unveiling the Investment Powerhouses
- Understanding the Chinese Company Stock Market in the U.S.
- Understanding CNN Ticker Symbols: The Ultimate Guide
- Master the Art of Trading: Understanding Market Index Symbols
- Top US Stocks Growth Sectors 2025: Future Investment Opportunities
hot stocks
 "Best Performing US Stocks: Top 5 fro
"Best Performing US Stocks: Top 5 fro- "Best Performing US Stocks: Top 5 fro"
- Silver Spot Prices: A Comprehensive Guide to U"
- Best Cheap US Stocks: Discover Hidden Gems for"
- Unlocking Potential: The Rise of Cannabis Stoc"
- The Largest Stock Exchange in the US: A Compre"
- Percentage of South Koreans Investing in US St"
- Buying U.S. Stocks from Australia: A Guide for"
- New US Stocks 2020: Exploring the Emerging Opp"
recommend
 Understanding the Stock Market to GDP Ratio in
Understanding the Stock Market to GDP Ratio in
Master the Art of Trading: Understanding Marke
The US Stock Market in the 1930s: A Decade of
US Price for ACB Stock: Comprehensive Guide an
Understanding CNN Ticker Symbols: The Ultimate
Momentum Stocks in the US Market October 2025:
Build Quality Housing Stock: Germany, US, and
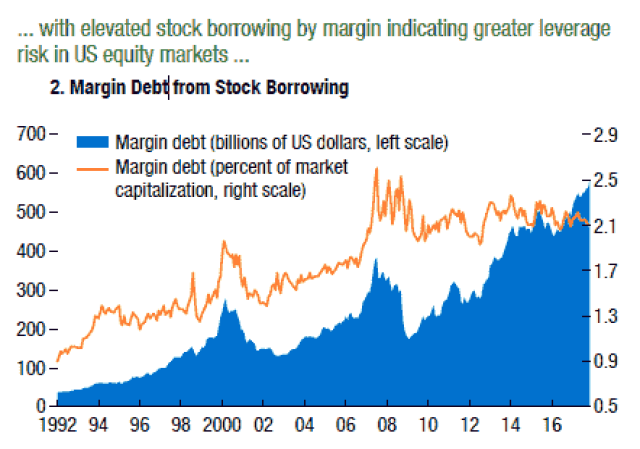
Best Cheap US Stocks: Discover Hidden Gems for
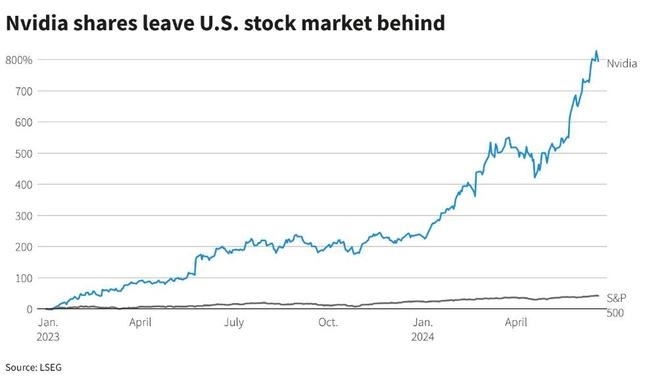
Understanding the Chinese Company Stock Market
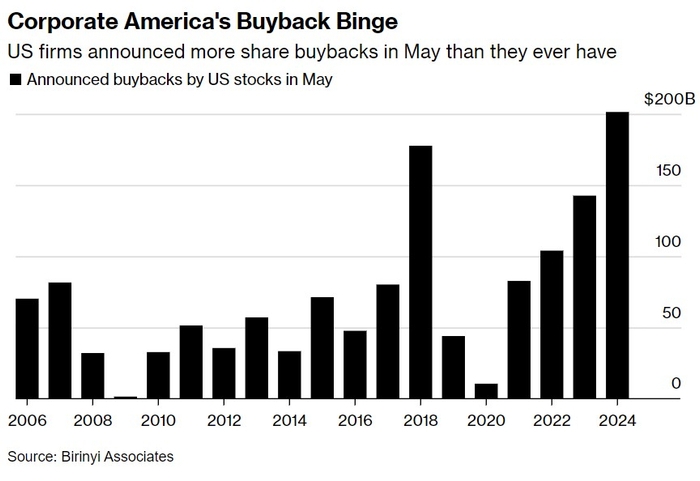
CNN Share Market: Navigating the Stock Landsca
Stocks US Today: Your Ultimate Guide to the Ho
tags
-
AllegedNon-USOpenHolidaysDelekSmallPurchaseBYDEarthClosedGoldEssentialCanTomorrowLNGChineseComprehensUnderstaGrowingRareFuturesAprilHolSchwabManyJonesDefinitiofromIndianMFCDaysTotalFoodSixth-GenerBogleheFallCitizensNintendoDidListTimings100verutodshareamerican10miniliveShausaTarCleanasdaqequityratioTraPriLucrRegSmarspreadHoldingToOptCom2022UnveilinaverageUndertodayFuCorreTradETPharmacequantitativeGaFuturSustainaAvGuidWhisBroadcFindLloanEarningcolacoca us stocks silver etf games us stock
like
- CNN Share Market: Navigating the Stock Landsca"
- Maximizing Total Return for US Stocks: Strateg"
- Number of Stocks on US Exchanges: A Comprehens"
- Unlocking the Potential of US E&P Stoc"
- Cotton Stocks: The Ultimate Guide to Understan"
- Unlocking the Potential of US Boxcar Stock: A "
- US Stock Exchange Chart: A Deep Dive into Janu"
- Coupang US Stock: A Deep Dive into the South K"
- "Greninja Toys R Us Stock: The Ultima"
- Unlocking the Potential of DRNK.PK: A Deep Div"

