you position:Home > new york stock exchange > new york stock exchange
Understanding the Tax on Stock Earnings in the US
![]() myandytime2026-01-19【us stock market today live cha】view
myandytime2026-01-19【us stock market today live cha】view
info:
Are you a stock investor looking to maximize your returns? It's crucial to understand the tax implications of your investments, especially the tax on stock earnings in the US. This article delves into the basics of how this tax works, its impact on your investments, and strategies to minimize your tax liability.
What is the Tax on Stock Earnings?
The tax on stock earnings in the US refers to the taxes imposed on the income generated from stocks, including dividends and capital gains. This tax varies depending on the type of stock, the holding period, and your income level.
Dividend Taxes
Dividends are the profits distributed by a company to its shareholders. In the US, dividends are taxed at a lower rate compared to ordinary income. The tax rate depends on your income level:
- Qualified Dividends: These are dividends that meet certain requirements set by the IRS. They are taxed at the lower capital gains tax rates, which are 0%, 15%, or 20% depending on your taxable income.
- Non-Qualified Dividends: These are dividends that do not meet the IRS requirements. They are taxed as ordinary income, which can be as high as 37%.
Capital Gains Taxes
Capital gains refer to the profit you make when you sell a stock for more than you paid for it. The tax rate on capital gains depends on how long you held the stock:
- Short-Term Capital Gains: If you held the stock for less than a year, the gains are taxed as ordinary income.
- Long-Term Capital Gains: If you held the stock for more than a year, the gains are taxed at the lower capital gains tax rates.
Strategies to Minimize Tax Liability
- Invest in Qualified Dividends: To benefit from the lower tax rate on dividends, invest in stocks that pay qualified dividends.
- Holding Period: To qualify for long-term capital gains tax rates, hold your stocks for more than a year.
- Tax-Loss Harvesting: This strategy involves selling stocks that have lost value to offset capital gains taxes on stocks that have gained value.
- Use Retirement Accounts: Consider investing in tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s, where gains are taxed at a lower rate or not taxed at all.
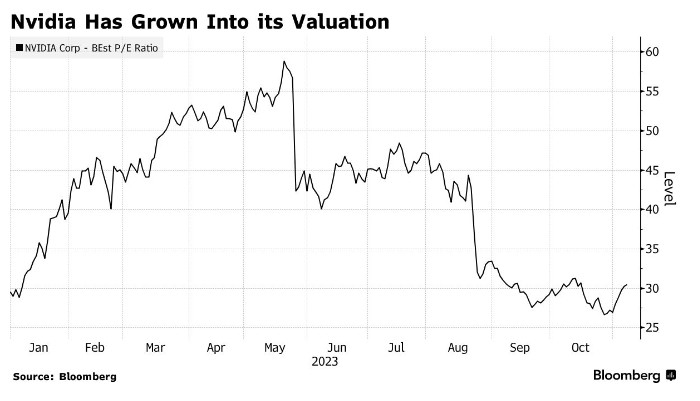
Case Study: Tax Implications of Selling Stocks
Let's consider a scenario where John holds a stock for one year and sells it for a profit. If he has a taxable income of $100,000, his short-term capital gains tax rate would be 37%. However, if he held the stock for more than a year, his long-term capital gains tax rate would be 20%, resulting in a lower tax liability.
Conclusion
Understanding the tax on stock earnings in the US is essential for any investor looking to maximize their returns. By familiarizing yourself with the different tax rates and strategies to minimize your tax liability, you can make informed investment decisions and potentially increase your net worth.
so cool! ()
like
- Total Market Capitalization: The Size of the US Stock Market
- Ticker Tape for US Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide
- Top Performing US Large Cap Stocks Over the Past 5 Trading Days
- Greenbrier Companies: A Leading Force in US Railroad Stocks
- Can F1 Visa Holders Invest in the US Stock Market?
- Stock Symbol for US Treasury Bonds: A Comprehensive Guide
- Can You Buy Nintendo Stock in the US? A Comprehensive Guide
- 2025 April 30th: A Deep Dive into the US Stock Market News
- US Dollar vs. Emerging Markets Stocks: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Stock Trade Transactions in the US: A Yearly Overview
- Best US Stock to Invest In for 2023: Top Picks and Analysis
- Can a Foreigner Buy U.S. Stocks? A Comprehensive Guide
hot stocks
 HSBC US Stock Trading Fees: What You Need to K
HSBC US Stock Trading Fees: What You Need to K- HSBC US Stock Trading Fees: What You Need to K"
- Top Momentum Stocks in the US Market August 20"
- Unlocking Opportunities with US Small Value St"
- Shionogi Stock US: A Comprehensive Analysis of"
- Unlocking the Potential of Barclays Bank US St"
- Does MGM Macau Affect MGM Stocks in US?"
- Unlock the Power of Free US Stock Data: Your U"
- "Can US Residents Open a Stock Accoun"
recommend
 Total Market Capitalization: The Size of the U
Total Market Capitalization: The Size of the U
Enbridge Stock: A Comprehensive Guide to Inves
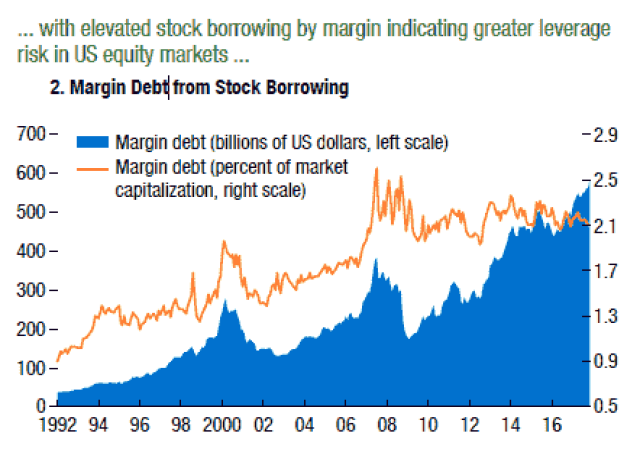
Current CAPE Ratio: A Deep Dive into the US St
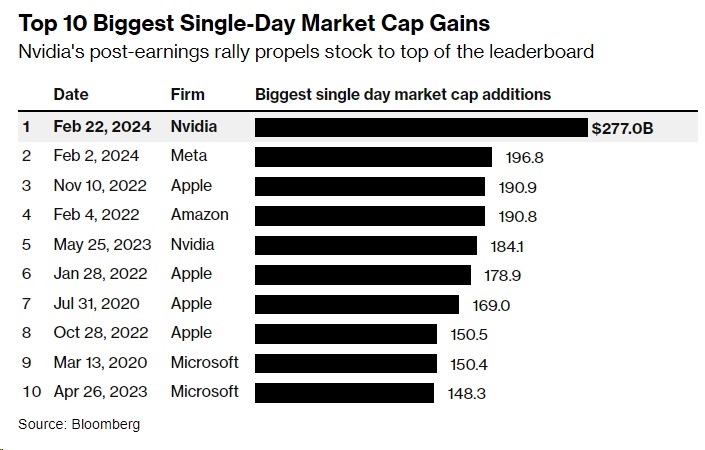
Invest 10,000 in US Stock Market in 1950: What

Stock Trade Transactions in the US: A Yearly O
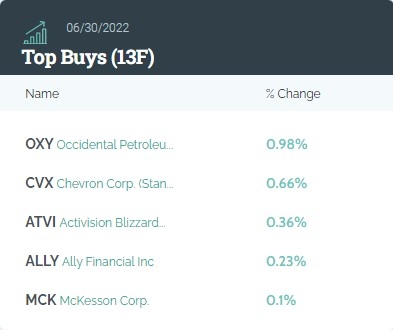
Independence Realty Trust: A Leading Player in

Alexion Pharmaceuticals: A Leader in US Biotec
Unlock the Power of Stock Screener US: Your Ul

Top Short Term Momentum Stocks in the US: Your
"Free Us Stock Trading: How to Maximi

US Crude Oil Stock Forecast: Insights and Pred
tags
-
AllegedNon-USOpenHolidaysDelekSmallPurchaseBYDEarthClosedGoldEssentialCanTomorrowLNGChineseComprehensUnderstaGrowingRareFuturesAprilHolSchwabManyJonesDefinitiofromIndianMFCDaysTotalFoodSixth-GenerBogleheFallCitizensNintendoDidListTimings100verutodshareamerican10miniliveShausaTarCleanasdaqequityratioTraPriLucrRegSmarspreadHoldingToOptCom2022UnveilinaverageUndertodayFuCorreTradETPharmacequantitativeGaFuturSustainaAvGuidWhisBroadcFindLloanEarningcolacoca us stocks games silver etf us stock
like
- Food Company Stocks: The Ultimate US Investmen"
- "How Many Stock Markets Are There in "
- Buying a Canada Stock Based in the US: What Yo"
- HSBC Stock Price US: Key Factors and Future Ou"
- Can You Buy CATL Stock in the US?"
- Maximize Your Investment Potential with Etoro "
- Understanding U.S. Stock Market Holidays: What"
- The End is Nigh for Us Stocks? A Deep Dive int"
- Energy Sector Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide fo"
- Samsung Vendor List: Companies on the US Stock"

